You have no items in your shopping cart.

- Home /
- Blog
How to Use Tibial Interlocking Nail for Effective Bone Healing?
The process of bone healing is complex and challenging. One effective technique to support this healing is the use of the Tibial Interlocking Nail. This method provides stability for fractured tibia bones. It is crucial in orthopedic surgery.
The Tibial Interlocking Nail allows for proper alignment of the bone. It comprises a robust metal rod inserted into the tibia. Screws interlock with the rod, providing additional support. This setup can significantly improve healing times and outcomes. However, the technique requires precise application.
Clinicians must apply the Tibial Interlocking Nail correctly. Improper placement can lead to complications. Issues may arise, such as infection or misalignment. Therefore, training and experience are vital. Surgeons often reflect on their previous surgeries to improve their skills. Even experienced professionals must keep learning to ensure patient safety and optimal healing.
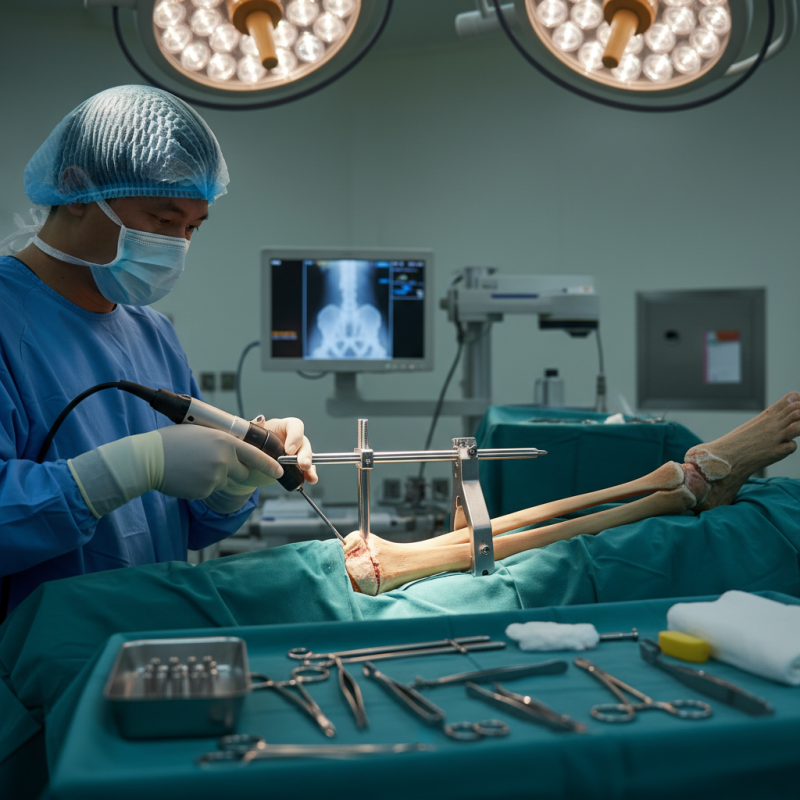
Tibial Interlocking Nail: Overview of the Procedure and Indications
Tibial interlocking nail is a popular technique in orthopedic surgery. It is often used for treating fractures in the tibia. The procedure involves inserting a metal rod into the medullary cavity of the tibia. This device stabilizes the bone and promotes effective healing. Proper alignment is crucial for success. Surgeons carefully select the entry point and angle for optimal placement.
Indications for this procedure vary widely. It is useful for both traumatic fractures and diaphyseal issues. Severe fractures with multiple fragments are also treated with this technique. However, it is not suitable for all patients. Certain conditions, like severe osteoporosis, may complicate healing. Surgeons must assess risks before proceeding.
The recovery process can be challenging. Patients often face pain and mobility restrictions. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor healing progress. Some patients experience delayed union or complications. These issues require reflection and potential adjustments in treatment. Understanding the intricacies of tibial interlocking nails is key for successful outcomes.
Preoperative Assessment for Tibial Interlocking Nail Surgery
Preoperative assessment is crucial for successful tibial interlocking nail surgery. It begins with a thorough patient evaluation. The healthcare provider must review medical history and current medications. Understanding any pre-existing conditions is important. Any history of infections or complications can affect outcomes.
Imaging studies, like X-rays or CT scans, help visualize the fracture. These images guide the surgical plan. Assessing the fracture type and alignment is key. Additionally, evaluating the soft tissue surrounding the fracture ensures a comprehensive approach. Factors such as swelling or skin condition must be noted.
Preparing for the procedure also includes discussions about anesthesia. Patients should voice any concerns regarding the process. This fosters trust and understanding. It's essential to set realistic expectations about the recovery timeline. Each patient’s healing experience differs.
Clear communication about possible risks and complications is vital. Addressing these points can help patients feel more at ease.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Tibial Interlocking Nail Insertion
The procedure for inserting a tibial interlocking nail is crucial for effective bone healing. This method is particularly useful for patients with unstable tibial fractures. Studies indicate that this technique has a success rate of up to 90% in achieving consolidation of bone fractures.
The first step involves proper patient positioning. The limb should be appropriately placed to allow access to the fracture site. After anesthesia is administered, a small incision is made over the tibia. Next, the nail is inserted through the cortex into the medullary canal. A challenge lies in ensuring the nail is aligned correctly with the fracture. Misalignment can lead to complications such as malunion.
Once the nail is in position, the locking screws are inserted to secure it. Accurate placement is critical; errors may result in further surgery. Continuous monitoring of the patient post-operation is essential. Complications, though rare, can occur. Common issues include infection and delayed healing, which require a proactive approach from the surgical team. Proper pre-operative planning and technique can significantly reduce these risks.
Effectiveness of Tibial Interlocking Nail for Bone Healing
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation Protocol for Bone Healing
Postoperative care is crucial for successful bone healing after tibial interlocking nail surgery. Patients should monitor their surgical site for any signs of infection. Swelling and tenderness are common initially, but they should gradually decrease. Keeping the leg elevated helps reduce swelling. Cold compresses can aid in managing discomfort during the first few days.
Physical rehabilitation begins with gentle exercises to regain mobility. Range-of-motion exercises help prevent stiffness. Patients should follow a structured program, focusing on gradual strength building. Walking can start with crutches, allowing gradual weight bearing. Pain levels must be managed effectively to encourage participation in therapy.
Some may struggle with adhering to rehabilitation protocols. It requires patience and dedication. Daily exercises can seem monotonous. It's essential to reflect on progress and set small goals. Everyone heals at their own pace. Keeping an open line of communication with healthcare providers can address concerns or barriers during recovery.
Complications and Considerations in Tibial Interlocking Nail Use
When using tibial interlocking nails, several complications can arise. Infection is a primary concern. The insertion site can become infected, leading to more severe complications. Ensuring sterile conditions during surgery is crucial to minimize this risk. Regular monitoring of the wound is also important. Any signs of redness or swelling should not be ignored.
Another issue is improper alignment. If the nail is not correctly placed, it can lead to malunion or nonunion. This situation complicates recovery and often requires additional surgeries. Surgeons must pay careful attention during the procedure to ensure the alignment is as accurate as possible. Utilizing imaging techniques can aid in this process, but limitations exist.
Post-operative care is as vital as the surgical procedure. Patients must follow rehabilitation protocols. They need to avoid putting weight on the leg for a prescribed period. Non-compliance can lead to setbacks in healing. Education on the importance of this phase is crucial. It’s a delicate balance between healing and too much activity too soon. Reflecting on these facets can help improve outcomes in tibial interlocking nail use.
How to Use Tibial Interlocking Nail for Effective Bone Healing? - Complications and Considerations in Tibial Interlocking Nail Use
| Complication | Description | Incidence (%) | Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infection | Soft tissue or bone infection following nail insertion. | 3-5% | Antibiotics, surgical debridement if necessary. |
| Nonunion | Failure of the bone to heal after nailing. | 10-15% | Bone grafting, revision surgery. |
| Malunion | Improper alignment of bone during healing. | 5-10% | Corrective surgery, physical therapy. |
| Hardware Failure | Breakage or loosening of the interlocking nail. | 1-3% | Removal of broken hardware, replacement if needed. |
| Neurovascular Injury | Damage to nerves or blood vessels near the surgical site. | <1% | Surgical repair, monitoring. |
